Working in content SEO for a news website is a unique experience. You’re generally working in a much faster-paced environment, particularly if you are in a national newsroom optimising pages for a major digital publication.
Whether you are on the news desk, competing with other sites to get your breaking news article into the carousel, or optimising a category page for a major celebrity to bring in head keyword traffic, no two days are the same.
You may be new to the world of news content SEO, or perhaps you’ve been doing it for a while. Perhaps you’re part of an established organisation, or you’re just starting out. Regardless of your position, there are a number of considerations to keep in mind as you deliver information to the public. Here are the most important ones…
1. Implement good breadcrumbs
As news production is so rapid, site architecture is more important than ever. Readers will be encouraged to click through to further stories or section pages, so having good breadcrumbs in place ensures they can take a step back if they want to.
This navigational aid assists with reducing bounce rates, doesn’t require the user to learn how to use the function and adds useful functionality without harming the overall design of the page.
Stick to the basic rules of thumb – don’t show more than three to five levels of breadcrumbs, use clear and descriptive labels and ensure the current page is highlighted so users know exactly where they are in the current hierarchy. Check out our guide to better SEO breadcrumbs for a comprehensive overview.
2. Create clickable bylines
Google’s EEAT guidelines indicate that authors need to demonstrate each of the criteria – experience, expertise, authoritativeness and trustworthiness. A greater weighting is placed on the author than the main content, so it’s vital to ensure that each writer on your news site can be clearly identified.
Typical practice is to include a byline on each article which the user can click on to view an author bio or portfolio. This page should ideally include an image of the writer, a full archive of their published works on the site and a section describing who they are.
The latter is particularly important, as it will serve as an overview of why the writer focuses on their chosen niche, what their experience is and ultimately why they are a trustworthy source. We have provided a full guide to optimising for EEAT.
3. Tag sponsored content
Some news sites will have sponsored content from time to time or on a regular basis, and it’s important to ensure it is properly tagged. If not, sites risk misleading users who will potentially become frustrated or lose trust in the brand upon discovering content is promotional in nature. This can lead to higher bounce rates and lower user engagement. What’s more, search engines like Google may penalise the site if it is seen to be using deceptive practices such as hiding sponsored content or misleading users.
There are a few ways to tag sponsored content. A specific HTML tag can be used to indicate that an article is sponsored – <meta name=”sponsored” content=”true”>. Alternatively, schema.org has a structured data markup which has been specifically designed for sponsored content:
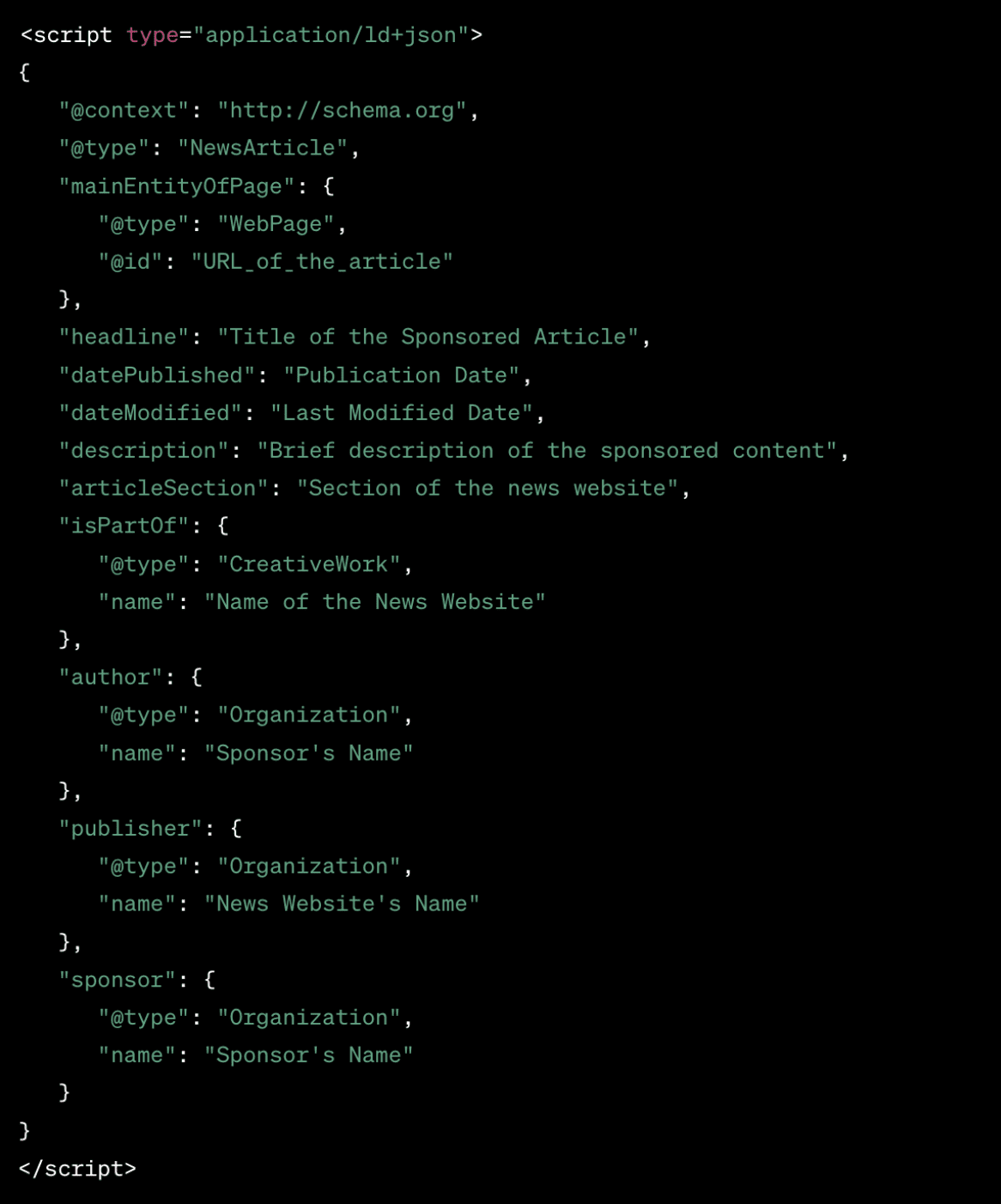
4. Add structured data to paywalls
News sites may implement paywalls for certain types of content, but it’s important to ensure these have been marked up correctly or search engines may identify them as cloaking. This deceptive practice involves presenting different content to search engines compared with what is shown to users.
To prevent this misunderstanding from happening, Google recommends ensuring it can see what’s behind the paywall. The search engine provides a guide to implementing structured data for subscription and paywalled content using schema.org JSON-LD. If sites want their paywalled content to be crawled and indexed, they should use this schema markup on all applicable pages.
5. Optimise category pages for head keywords
Over time, news content will be built up that can be assigned to specific categories. Instead of ignoring these pages, it’s worth considering that category pages can be an important organic traffic stream on publisher websites. For example, if a site has a category page for ‘celebrity news’ then this page can be optimised in a number of ways.
First, conduct keyword research to indicate that the right terms are being used. For example, you may find that other phrases have higher search volumes. To find out more, read our guide on how to prioritise keywords for SEO.
Then create informative text for the category which provides a clear summary of what the page offers. Ensure all of your relevant pages have been pulled through, and confirm that the on-page elements, such as the title tag and URL structure, are optimised.
6. Manage tagging to avoid thin page indexing
The tagging feature can be a double-edged sword. While it is a useful tool for organising multiple articles on the same theme, it can quickly get out of control if there are multiple writers using different variations of a word or phrase. Instead of having useful tagging which allows search engines and users to discover related articles on a topic, there is instead a mess of disorganized tags.
If tagging is allowed to run rampant, sites run the risk of having tag or topic pages with just one or two articles populating it and little or no contextual content. This can result in large numbers of thin or no content pages, which can impact crawl budget.
There are two approaches which can be taken – either remove tagging as an external feature on the site or have strict rules about who can approve and create new tags.
7. Use rel=canonical tag for syndicated articles
It’s common practice these days for publishers owning a network of publications to syndicate an article across several, most or all of the sites in order to improve its reach. However, if the original article is not indicated with the correct canonical tag then this can confuse search engines, as they may mark the ‘wrong’ site as the one to prioritise in SERP for the article.
While syndicating content is not against Google’s guidelines, it is advised to use the right canonical tag if you want the search engine to understand which article is the original. To do this, you can embed a rel=canonical tag into the HTML of article duplicates which appear on other sites within the network.
Alternatively, you could add a no index robots meta tag within the HTML of the article duplicates to indicate to search engines that the syndicated content should not be indexed in SERPs. To find out more, check out our guide on technical fixes for duplicate content.
Need help with your SEO news production?
If you’re thinking of launching a news section for your site, or you’re an established brand encountering SEO issues you could do with some consultancy on, we’re here to help. Get in touch with us and we’ll get the conversation started.
Slots are starting to fill up for our Free Acquisitions Workshops. These analyses allow you to immediately understand what can be improved – and we will tell you how to implement the fixes right away.